Introduction
The Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination of the United States (COMLEX-USA) is the pathway to licensure for osteopathic physicians seeking to practice medicine. It is the principal means by which the NBOME delivers on its mission to protect the public by providing assessment of competencies for osteopathic physicians and related health care professions.
The COMLEX-USA examination series is designed to assess osteopathic medical knowledge, fundamental clinical skills, and other foundational competencies considered essential for the practice of osteopathic medicine. The primary and intended purpose of COMLEX-USA is for licensure of osteopathic physicians, and COMLEX-USA is accepted for medical licensure in all 50 states and US territories.
The COMLEX-USA Blueprint emphasizes the competencies required for generalist physicians to deliver safe and effective osteopathic medical care. The foundation of COMLEX-USA is the osteopathic approach to patient care. Its evidence-based design assures state licensing boards and the public that a DO has demonstrated minimal competence by passing a series of national standardized examinations designed for the practice of osteopathic medicine. Aligned with the education and training pathway of a DO, passing Levels 1 and 2-CE of COMLEX-USA is required for graduation with a DO degree and entry into residency training.
In the years since its implementation, the COMLEX-USA Blueprint has been reviewed and revised regularly to reflect the practice of osteopathic medicine, consistent with the recommendations of the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing 2014 established by the American Educational Research Association (AERA), the American Psychological Association (APA), and the National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME). The design of COMLEX-USA has transitioned from its initial conjunctive, discipline-based content organization in 1995 to today’s innovative COMLEX-USA Blueprint.
The current COMLEX-USA Blueprint, implemented beginning with Level 3 in September 2018, features a framework that maps content to competency domains and clinical presentations. The COMLEX-USA Blueprint and test specifications for each exam were then introduced into Level 1, Level 2-PE, and Level 2-CE with the test cycles beginning in 2019.
Further information on the development of the COMLEX-USA Blueprint is described in “Evidence-Based Redesign of the COMLEX-USA Series” (John R. Gimpel, DO, MEd; Dorothy Horber, PhD; Jeanne M. Sandella, DO; Janice A. Knebl, DO; John E. Thornburg, DO, PhD), The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, April 2017, Vol. 117, pp. 253–261. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2017.043.
Foundation for COMLEX-USA
Osteopathic principles and practice continue to form the foundation of COMLEX-USA within both of its dimensions.
Tenets of Osteopathic Medicine
- The body is a unit; the person is a unit of body, mind, and spirit.
- The body is capable of self-regulation, self-healing, and health maintenance.
- Structure and function are reciprocally interrelated.
- Rational treatment is based upon an understanding of the basic principles of body unity, self-regulation, and the interrelationship of structure and function.
Two Distinct Dimensions
COMLEX-USA examination content is organized by two dimensions:
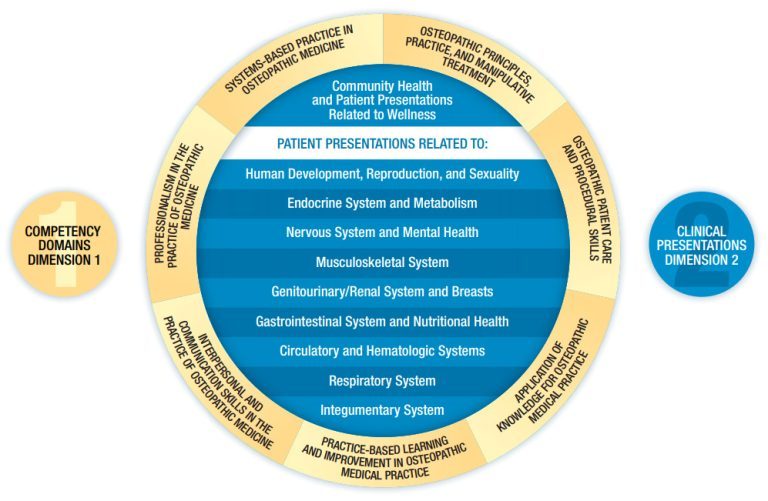
Dimension 1: Competency Domains
Dimension 1 of the COMLEX-USA Blueprint consists of the seven COMPETENCY DOMAINS, the related sets of foundation abilities representing the required elements and outcomes that define osteopathic knowledge, skills, experience, attitudes, values, behaviors, and established professional standards. Each competency domain is described in detail with required elements and measured outcomes. For each examination in the series, test specifications outline the content coverage as it relates to these seven competency domains.
Dimension 2: Clinical Presentations
Dimension 2 of the COMLEX-USA Blueprint consists of the 10 CLINICAL PRESENTATIONS, which represent the manner in which a particular patient, group of patients, or a community present(s) for osteopathic medical care. These high-frequency, high-impact categories are based on evidence from osteopathic medical practice. Patient presentations span all relevant age categories, special populations, and varied clinical settings. Each clinical presentation is described in detail, further categories into topics with accompanying guides, and provides examples illustrative of the presentation. For each examination in the series, test specifications outline the content coverage as it relates to the 10 clinical presentations.
Blueprint Schematic
Licensure Assessment Aligned With Medical Education Pathway
Candidates will be required to demonstrate minimal competency across each of the seven competency domains. The outline for implementation of the two-decision-point, competency-based COMLEX-USA Blueprint is depicted here:
COMLEX-USA Examination Program
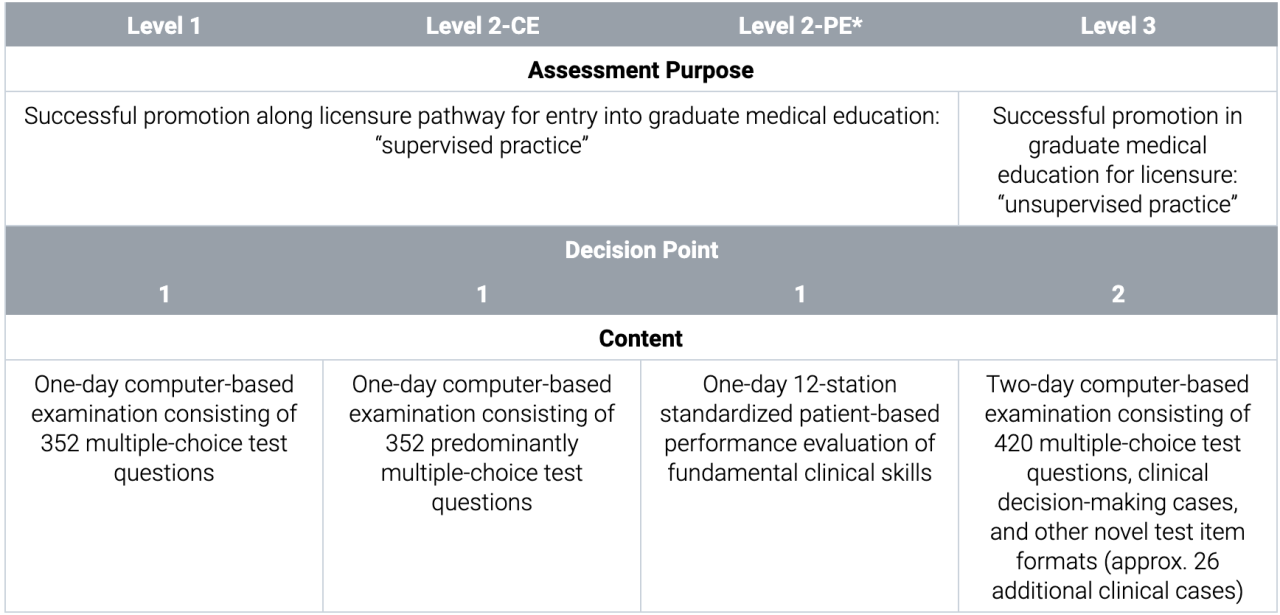
* Please note that the Level 2-PE has been discontinued. For Level 3 eligibility pathways and details, please visit this page.
Test Specification Percentages for Each Examination
| Dimension 1: Competency Domains | Level 1 | Level 2-CE | Level 2-PE+ HUM* · BM/BM* | Level 3 | Series Min. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Osteopathic Principles, Practice, and Manipulative Treatment | 12% | 10% | 0% · 15% | 10% | 10% |
| 2. Osteopathic Patient Care and Procedural Skills | 6% | 30% | 0% · 25% | 40% | 25% |
| 3. Application of Knowledge for Osteopathic Medical Practice | 60% | 26% | 0% · 15% | 15% | 30% |
| 3.1 Foundational Biomedical Sciences Knowledge Base | 75% | 25% | – | 10% | – |
| 4. Practice-Based Learning and Improvement in Osteopathic Medical Practice | 4% | 7% | 0% · 5% | 8% | 5% |
| 5. Interpersonal and Communication Skills in the Practice of Osteopathic Medicine | 3% | 5% | 60 · 20% | 5% | 10% |
| 6. Professionalism in the Practice of Osteopathic Medicine | 3% | 7% | 30% · 5% | 6% | 5% |
| 7. Systems-Based Practice in Osteopathic Medicine | 2% | 5% | 0% · 5% | 6% | 5% |
* HUM: Humanistic Domain | BM/BM: Biomedical/Biomechanical Domain
| Dimension 2: Clinical Presentations | Level 1 | Level 2-CE | Level 2-PE* | Level 3 | Series Min. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Community Health and Patient Presentations Related to Wellness | 12% | 12% | 14% | 12% | 12% |
| 2. Human Development, Reproduction, and Sexuality | 5% | 5% | – | 5% | 5% |
| 3. Endocrine System and Metabolism | 5% | 5% | – | 5% | 5% |
| 4. Nervous System and Mental Health | 10% | 10% | 14% | 10% | 10% |
| 5. Musculoskeletal System | 13% | 13% | 14% | 13% | 13% |
| 6. Genitourinary/Renal System and Breasts | 5% | 5% | – | 5% | 5% |
| 7. Gastrointestinal System and Nutritional Health | 10% | 10% | 14% | 10% | 10% |
| 8. Circulatory and Hematologic Systems | 10% | 10% | 14% | 10% | 10% |
| 9. Respiratory System | 10% | 10% | 14% | 10% | 10% |
| 10. Integumentary System | 5% | 5% | – | 5% | 5% |